Google rolls out a couple major algorithm updates every couple of years. However, these aren’t the only algorithm updates. Each day, Google makes tiny tweaks to its search algorithm. These tweaks are continuous and are mostly unnoticed. In fact, according to Moz, Google changes its search algorithm around 500–600 times each year.
Understanding how and when Google algorithm is updated and what impact it will have on your website’s ranking is one of the most difficult tasks that SEO experts have to do.
To help you stand firm and future proof your SEO efforts, you need to understand the 6 most significant Google algorithm updates:
- Panda
- Penguin
- Hummingbird
- Caffeine
- Rankbrain
- Fred
Let’s discuss each of them in detail.
1. Panda
Google Panda was rolled out on 24th February 2011, and is a major algorithm update. Panda is a content-related update that targets websites with low-quality, duplicate, and thin content.
Panda is was regularly updated before it became a permanent part of the search engine algorithm. The last update was released in July 2015 known as Panda 4.2.
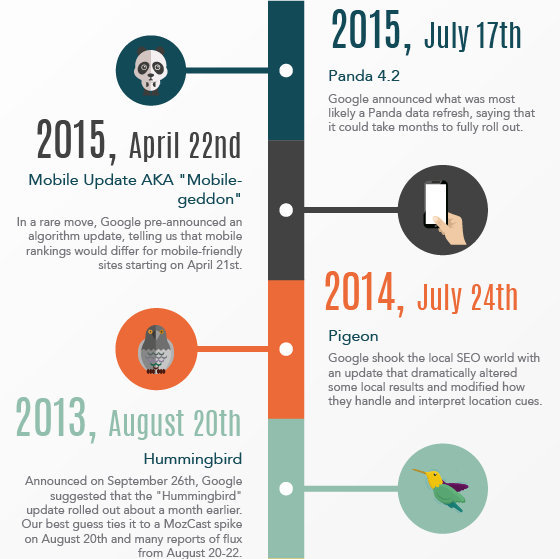
So what does Panda do and how can you avoid getting a penalty?
It’s all about content. Period.
Panda has nothing to do with backlinks. Most people assume that every penalty is related to backlinks. This isn’t true.
Google Panda algorithm update ensures that no website with poor content makes it to the top of search engine results pages. It will, therefore, target all the websites that have:
- Duplicate or plagiarized content
- Content that is spun and not readable
- User-generated spam content
- keyword stuffed content
- Low click-through rate (CTR)
- High bounce rate
- Poor design and navigation
- Security issues
- Slow site speed
If your website has low-quality content, you’re more likely to receive a Panda penalty which will result in rankings drop like this.
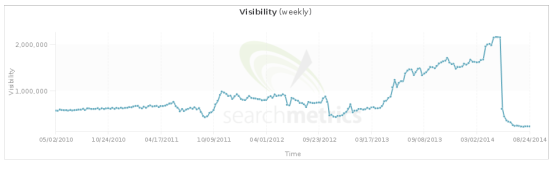
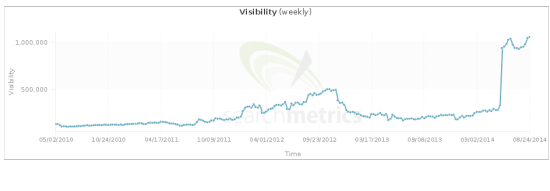
Here is a real example.
An ecommerce website was hit by Panda in July 2015. Organic traffic decreased by 40% despite having 4,000 new web pages being added to the website. This was a clear indication that it was hit by Panda.
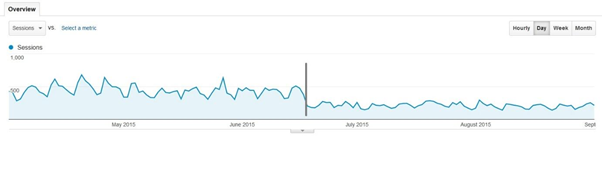
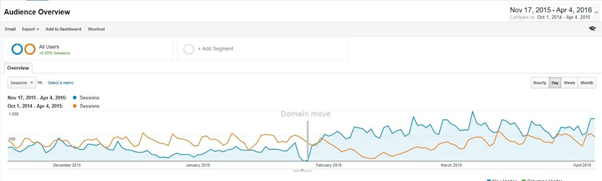
In order to stay safe from Panda, stick to useful and engaging content.
2. Penguin
Penguin update was launched in April 2012. The primary objective of this algorithm update was to target websites having spammy backlink profile. Unlike Panda, Penguin is strictly related to backlinks and nothing else.
After the first rollout in 2012, there had been several updates to Penguin. It was officially made a part of Google’s core algorithm in September 2016 and it now works in real-time. This final update is known as Penguin 4 and just like Panda there will be no future updates as it is now part of core algorithm.

Penguin punishes websites that do any of the following:
- Create or build spammy backlinks
- Backlinks from irrelevant websites
- Pay for backlinks
- Have over-optimized anchor text
If you’re doing any of the above, you’ll probably see a decline in rankings and a significant reduction in organic traffic like Metamorphosis Design.
The website was hit with Penguin in 2012.
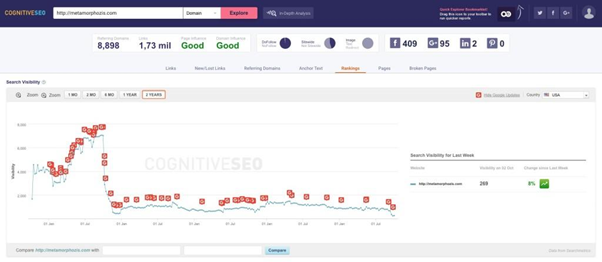
And, it was a victim of Penguin 4 as well.
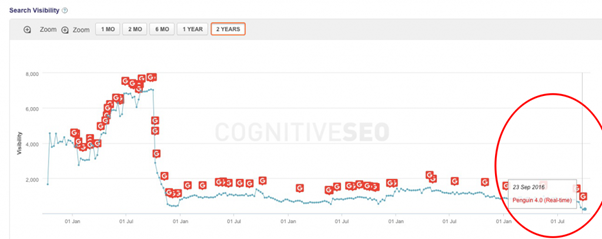
As much as 90% of total backlinks are unnatural.
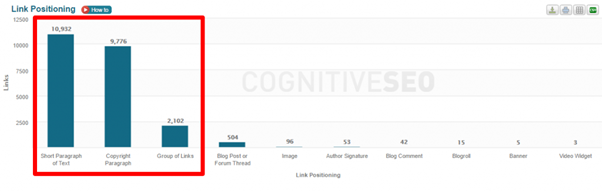
If you’re doing anything like this, expect a similar outcome. Avoiding Penguin penalty is simple: don’t build links unnaturally. It’s easier said than done.
Here are a few tips that will save you from getting a Google Penguin penalty.
- Never buy links.
- Get links from relevant websites only.
- Diversify your anchor text as much as you can. Refrain from using your primary keyword as anchor text.
- Take a close look at site-wide link ratio.
- Say no to PBNs.
- Low-quality backlinks such as blog comments and Web 2.0s are dangerous as hell.
Since Penguin is now a part of Google’s core algorithm, this means the impact of a penalty is instant. The moment Google finds that your backlink profile is manipulative, you’ll see a decrease in rankings.
If you have been hit by Penguin, unfortunately, here is what you should do to get back on track as soon as possible.
- Get rid of all the unnatural and spammy links.
- Use Google’s Disavow tool.
- Acquire new links naturally.
3. Caffeine
Google announced its Caffeine update back on June 8, 2010. It was one of the major algorithm updates rolled out. It was related to Google’s new indexing system which was updated.
The new index was efficient, fast, and fresher.
Google was able to add new and fresh content to its index in seconds as compared to a previous delay of as much as a couple weeks. The new index takes into account devices and media types too.
Caffeine, therefore, more than an algorithm update – it was a complete rebuild of their entire index system. This update didn’t impact any websites, it didn’t penalize websites, and it didn’t have any major impact on search results.
This update was all about making fresh content available in search results more quickly. So there isn’t anything that webmasters have to do in order to stay ahead of their competitors.
Caffeine is the index system that is still used today and this is the reason why you see pages that are published a few minutes ago in search results.
Thanks to Caffeine – the happy update.
4. Hummingbird
Another algo update by the name of an animal…you get the picture.
Google launched Hummingbird on 22 August 2013 with the aim of focusing more on understanding the meaning behind the search query instead of just keywords or phrases.
The idea was to make search engine results ‘precise and fast’ just like a hummingbird.
This update helps Google better understand search queries and return pages that are most relevant to what a searcher is interested in based on searcher’s intent.
You can rank for search terms if you haven’t used the exact keyword (or any related keyword) in the copy. It is done with the help of:
- Latent semantic indexing
- Synonyms
- Co-occurring
Websites with poor content, keyword stuffing, and exact match keywords aren’t appreciated after this update. Why?
Because such websites intend to focus concepts and practices to rank for certain keywords.
It doesn’t work anymore.
Although the keywords give you insights as to what the intent will be. When it comes to Hummingbird update, there are three elements that stood out:
a). Informational query: Selecting the right keywords for your campaigns may appear difficult, time consuming and confusing if you don’t know how to go about it. The good news is that the hummingbird update makes it a lot easier to understand why searchers are interested in a particular keyword.
For informational keywords though, these tend to provide information and you can identify them by their modifiers such as:
- How to
- Signs of
- Tips
- Learn to
- Free
- ways
- what is
- Define
- Meaning of
etc.
When searchers use any of these modifiers in their query, it means they are not likely going to purchase any product at the moment. But rather, they want free information.
This graphics show some examples of informational keywords:
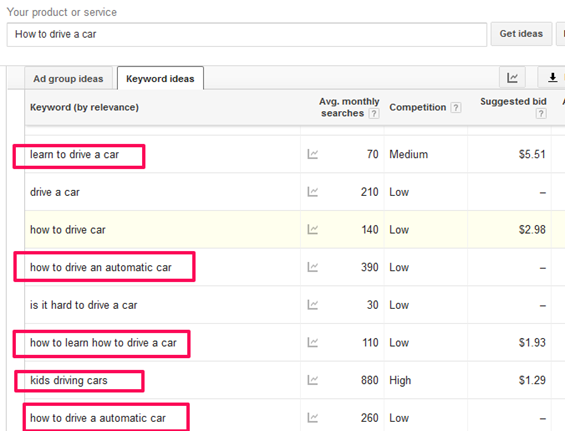
Essentially, informational keywords usually have high-search volume. So, it makes sense to target them in your content while addressing the primary purpose.
Provide enormous value (after all, the searcher is looking out for rich information). Make your content detailed, and use supporting visuals (graphs, charts, illustrations, screenshots) to improve the perceived and real value of your content.
b). Navigational query: Navigational keywords are termed “go keywords.” These are keywords that users who have knowledge about a particular brand uses.
When searchers includes a company or brand name to their query, it means they want to navigate to the company website or learn more about the company. They are aware of this company’s product already. For example, Domino’s Pizza.
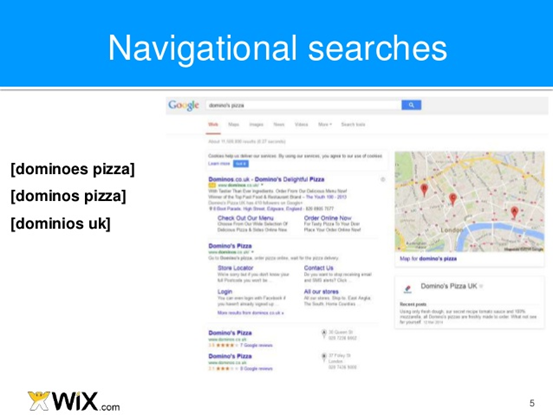
Of course, you may try to rank in Google search engine for your competitor’s brand names if they are popular — but be careful not to infringe of their rights.
Except the brand or product is well-known, navigational keywords don’t have a high search volume. But they drive one of the most targeted traffic and leads ever.
c). Transactional query: As the term implies, a transactional query is useful for commercial sites. These queries show the searchers who have the intent to buy a product, make a transaction, or has made a decision to try a particular service.
Transactional keywords are usually long-tail, don’t have high search volume (for most industries) but they are guaranteed to drive your conversions to the roof.
They usually include modifiers like:
- Reviews
- Buy
- Purchase
- Subscribe
- For Sale
- Where to get
- Comparison
- Price of
- Cost of
- Quotes
etc.
Here are some examples of transactional keywords or queries:
- Get insurance quotes
- Subscribe to new york times
- Buy blue Denim jeans
- Where to each Pizza in LA
- Wooden watch reviews
Note: In all of this, pay more attention to the intent (i.e., purpose) behind the keyword. Answer this question, “why are people searching for this keyword?” That’s what the hummingbird update is all about.
Here is an example. The searcher’s intent is to find nearest Starbucks so Google is showing search results with actual Starbucks locations. The first two search results don’t have the search term in their copy or description but they’re still ranking for this query.
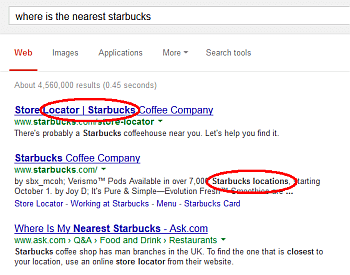
Here is what you’re supposed to do in order to avoid any Hummingbird penalties.
- Think about concepts instead of keywords.
- Write for readers without even thinking about keywords. If you write a blog post on silver laptops, it will rank for relevant queries no matter what.
- Avoid keyword stuffing.
- Understand your audience’s language and write content accordingly.
If you follow the simple tips above, you should be able to deal fairly with Hummingbird compared to Panda and Penguin — and also make the necessary tweaks to your SEO strategy for Hummingbird.
5. RankBrain
Rank Brain is a machine-learning artificial intelligence component of Google’s core algorithm (Hummingbird). RankBrain was rolled out on October 26, 2015. It filters search results by teaching itself.
The whole purpose of RankBrain is to understand searcher’s intent, the search query, and return most appropriate results using AI.
It’s an artificially intelligent component which makes it one of the most powerful updates ever. It takes data and signals from several sources and returns most suitable search results.
According to the Bloomberg article that first introduced the term RankBrain, it is the third most important Google ranking factor:
“RankBrain is one of the “hundreds” of signals that go into an algorithm that determines what results appear on a Google search page and where they are ranked. In the few months it has been deployed, RankBrain has become the third-most important signal contributing to the result of a search query.”
RankBrain is an AI-empowered algorithm that Google developed to sort the search results in its index. This machine learning system now makes it a lot easier for Google to understand what a particular query means, and provide the right answers (i.e., search results) for the user.
RankBrain serves more accurate results in the organic listings than humans beings. Google conducted a study and asked a group of Google Engineers to identify the best page for a search query. On the other hand, RankBrain was also the same question.
It may sound unbelievable but it’s true: RankBrain gave a more accurate answer than brainy Google engineers by 10%, according to Bloomberg.
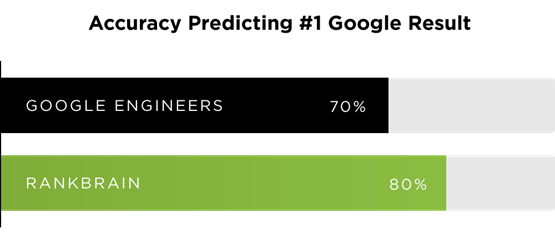
So there’s no denying the fact that RankBrain works and if you optimize according to its guidelines, your content pages will get more clicks in Google and, of course, improved rankings.
Essentially, RankBrain plays two important roles in the search:
- Dissecting, understanding, and interpreting keywords
- Analyzing and measuring user satisfaction on the page
When it comes to understanding keywords, Google was somewhat limited in the past. Because it could match the words in the query the words on a page and then decide whether or not that page is relevant, useful, and timely.
But when RankBrain was introduced, everything changed. It’s no longer about matching words in the query with those on the page, RankBrain can understand what a search user actually meant when he searched for, say:
“Learn salsa dance steps”
RankBrain now thinks like a human world, maybe better.
So how do you ensure that you’re optimizing your pages properly in a way that RankBrain can understand, interpret, and send you more traffic?
It all boils down to satisfying users.

When people visit your website, Google collects their data and uses it to gauge how happy and satisfied they are with your website.
Remember that RankBrain still has its flaws, so it relies on humans to make most of its decisions. How?
Let’s say that your content page ranks #1 in Google. Excited, right?
Well, if you get the clicks and a lot of people to your page and they stick around, this will send a signal to Google that you probably have useful content that users like. In this case, your rankings will be sustained.
If, on the other hand, the same people landed on your page, and bounced off, over time, Google will push your ranking down and replace it with another page that satisfies the user.
For RankBrain, the most important factors are the user engagement metrics such as:
- Organic Click-Through-Rate (CTR)
- Average time on site (Dwell Time)
- Bounce Rate
- Pogo-sticking
It’s your responsibility as a website owner and SEO professional to focus on these user engagement metrics — doing so will help you improve your organic visibility and build a profitable business.
6. Fred
It’s the most recent update rolled out in on March 8, 2017. It wasn’t, however, officially announced by Google rather it was communicated via Twitter dialogue.
Here are a few screenshots of conversations that took place between Google officials and SEO experts.
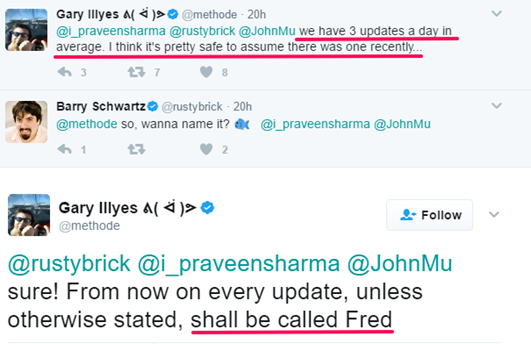
It’s a massive update that hit several websites. It targeted websites having too many ads and affiliate links, low-quality backlinks (like PBNs), and poor content.
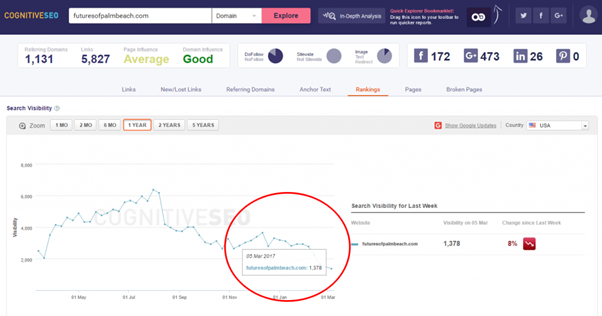
Here is a website that lost up to 90% of organic traffic in March 2017. The ads are highlighted yellow.

Clearly, it is an ad-heavy website that offered little to no value to the readers.
It doesn’t mean that you should remove ads and affiliate links, you can and you should but you should offer high-value content to readers.
Here is what Barry Schwartz said about the Fred update:
“About 95 percent of the sites that got hit were ones with content that looks to be written for ranking purposes and then has ads and/or affiliate links sprinkled through the article…they seem to have content on a vast array of topics that are not adding all that much value above what other sites in the industry have already written.”
There are several sites that were hit like this one.
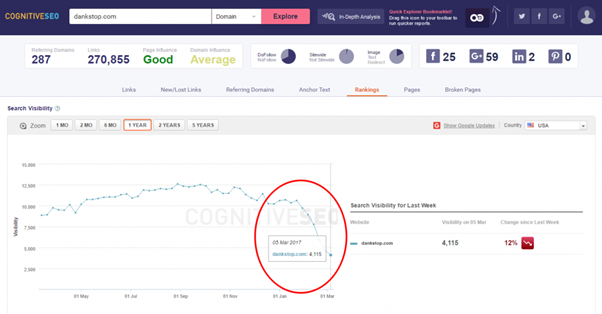
And this one.
Here is what you’re supposed to do if you don’t wish to become Fred’s next prey.
- Don’t build low-quality backlinks and refrain from spammy links.
- Get rid of all poor backlinks, if you have any.
- Minimize ads per page.
- Ads shouldn’t be a hurdle to user experience or they shouldn’t be manipulative.
- Publish high-quality content that delivers value. Thin content is a big no.
- Deliver exceptional user experience.
Fred hasn’t been officially announced by Google yet but it did happen and it is a reality. Don’t take it lightly.
Site Structure for SEO