Search engines want to provide exceptional user experience to their searchers. They prefer showing most appropriate websites with perfect structure so that the need of the searcher is satisfied. Website structure, however, is often overlooked.
Let’s explore a few of the benefits:
1. A good site structure enhances user experience
If readers are unable to find what they’re looking for, they will leave your website.
The structure is the backbone of your website. It makes navigation easier. It helps readers find what they’re looking for. They don’t feel lost.
This is what makes them stick around.
If you want to improve user experience, keep focus on these elements:
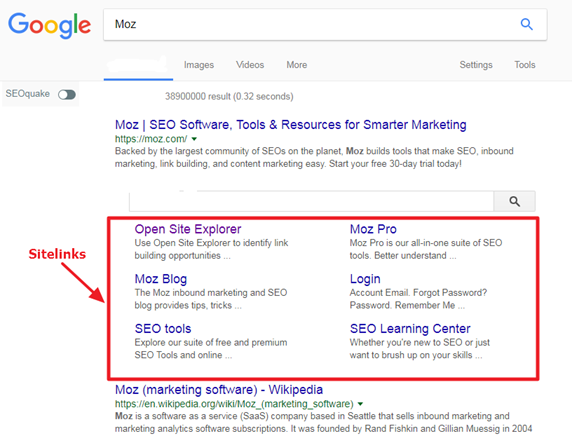
a). Sitelinks: To better provide good experience for users in the search results, you need sitelinks.
Sitelinks can make a huge impact on your click-through rate. They make your website easy to navigate, redirect users to the right information, boost your online reputation and branding, and helps you rank better in the search engine results pages (SERPs).
Sitelinks are really important. You often find them in the organic search listings:
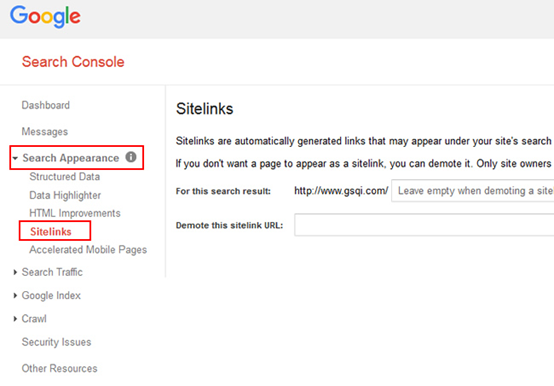
The easiest way to get sitelinks is by logging into your Google Search Console account, fill in a few fields and that’s all.
This path:
Google Search Console > Sitelinks > Add or demote site links
If your website has a poor structure, it’ll be difficult to search engines to give you sitelinks, and consequently, you’ll be losing out on a lot of targeted traffic, higher CTR, and increased rankings.
b). White space: Your website needs some breathing space. The white space (or negative space) is that blank section of your page. Most online entrepreneurs think that these unused real estate out to be used for banner advertising or to display sponsored ads.
The concept of white space isn’t limited to unused areas of your website that are white. But rather, any unused section of your website — be it white, read, blue, or any of your favorite color. Apple uses white space on their homepage to create memorable experience for users who wants to buy the iPhone X or any of their products.
Here’s the truth: white space is critical to great design. It makes your content easy to consume, more legible, while giving the user an opportunity to see all the elements surrounding the text.
Data from Crazy Egg shows that white space around text and titles boosts user attention by 20%. This percentage is high especially when you consider that humans attention span is 8 seconds, which is a second less than a goldfish’s.
For the best user experience on your website, make sure you use plenty of white space to make your website feel modern, fresh, and open. In turn, this will cause your website visitors to stick around consuming your content.
There’s really no downside to having plenty of white spaces on your website. Except that it takes up space.
c). Your page URL should match your site structure: User experience goes beyond what happens within the content, the URL is equally important. Make sure your URL follows the site hierarchy.
For example, if you own an online store and you’re selling women’s pink hoodie dress, your URL may look similar to this:
www.youronlinestore.com/dresses/womens-dresses/womens-pink-hoodie-dress
The URL is now broken down and categorize as follows:
Category > Sub-Category-Product.
This pattern is ideal for search engine crawlers to understand. It’s also the best way to structure your pages, name your URLs, and aid navigation on your website.
Content Marketing Up is a good example of a website with URL that matches site structure.
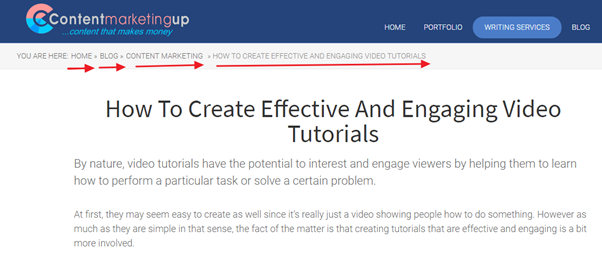
But more than that, users are also able to navigate back to the sub-category or category if they want to check out other products. This can lower your bounce rate and increase dwell time (i.e., average time spent on a page).
d). Use hyperlink differentiation: If you want the user or reader to click your link, then you must differentiate it from other texts. Even though underlined and colored text can attract the user, you still have to use a popular color that can be easily identified as a link.
In a research conducted by Karyn Graves, she concludes that the regular web user sees and understands that an underlined text with a blue color is probably a link and knows to click them.
That means you should use blue colors on your links if you want to guide the user properly, and nudge them to click on your links. Even the popular media sites like Inc, Fast Company, LinkedIn, Entrepreneur, and the like uses blue to differentiate clickable links from other regular text.
e). Interlink your pages: Is it possible to enhance user experience and ensure that your site structure is good for both users and search engines? Yes you can!
Start by interlinking your pages. When you create a new post on your blog, use a relevant term, keyword, or brand name to reference and link to your older posts. The more pages you interlink, the more you’re able to spread link juice among the pages.
Other factors such as page speed, using attractive call-to-action, using bullets and subheadings to break up large chunks of text or paragraph are all important when you’re delivering a good user experience.
2. A good site structure means better crawling
Search engine crawlers don’t see a website the way humans do. For them, it’s just text and codes. A proper structure with interlinking, hierarchies, pages, permalinks, etc. help crawlers find all the content on your website and index it.
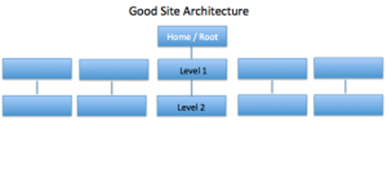
Here is an example of what makes a good site structure that will be easier for search engine crawlers.
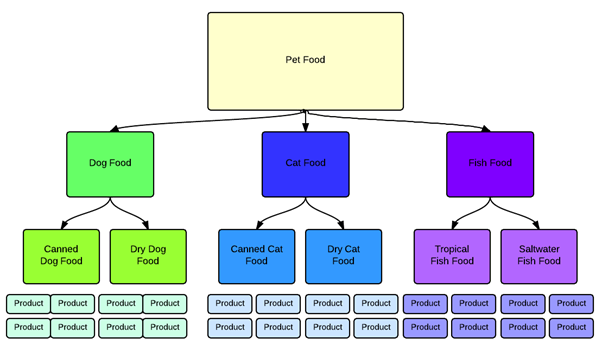
How does it actually happen and what steps you should take to ensure crawlability and fast indexation?
Let’s dig a bit deep.
How website architecture impact crawlability and indexation
In order to understand how your website’s architecture impact crawlability and indexation, you need to have a clear understanding of what crawlability and indexation means.
Here is what Google says about crawlability:
“Crawlers look at web pages and follow links on those pages, much like you would if you were browsing content on the web. They go from link to link and bring data about those web pages back to Google’s servers.”
And when these web pages are brought back to Google’s servers, they’re indexed and are returned in search results.
Crawlability, thus, refers to search engine’s ability to access and crawl content on your website.
Indexation refers to the ability of a search engine to add a webpage or website to its index.
It means if your website has been crawled, it isn’t necessary that all the web pages on the site will be indexed. A website that has a poor structure with web pages poorly linked, most of them won’t be indexed while a website having good structure will have its all pages indexed in the first go.
Only websites that are indexed appear on search results page.
So what does a good site structure looks like that will be easier to crawl and index?
Here is an example.
The same site can be structured like this too but in this case, crawlers have to move through 7 different pages to crawl all the pages on your website. It gets tough.
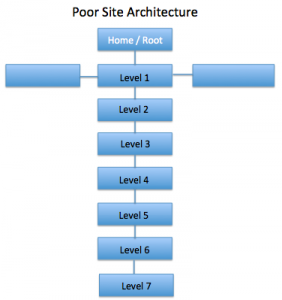
Website structure refers to how individual pages and subpages are linked to one another and how your entire website is set up. Poor, inconsistent, broken, and deep linking will result in poor crawlability because crawlers cannot find, reach, and index all the pages on your website.
In reality, crawlability and indexation depend entirely on your website’s structure – and nothing else. Googlebot is the name of the crawler (spider) that Google uses to crawl websites.
The Technology behind Googlebot
To fully understand crawlability and indexation, you have to understand how Googlebot works and what technology it uses.
Googlebot is the official web crawling bot used by Google to discover new web pages which are then added to the index for future use.
The technology behind Googlebot is Chrome 41, according to Ilya Grigorik from Google. This was announced recently so it is now easier than ever to work with crawlability issues. All you have to do is install Chrome 41 and see how your website looks.
Simple.
You can now easily fix crawl-related issues by checking your website in Chrome 41. It searches all the files and folders on your website and crawls them.
How Website Speed Affect SEO
Google announced back in 2010 that website speed is a ranking factor. It isn’t important for Google but research shows that websites with high loading time negatively impact conversions, increase bounce rate, and lower average time on page.
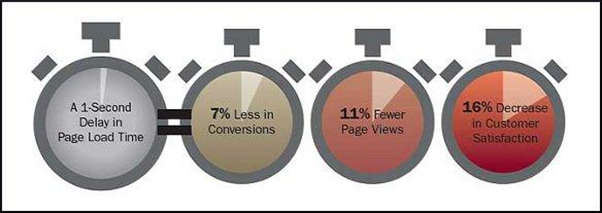
It isn’t about minutes instead it is all about seconds.
But why does Google care so much about website speed?
Google wants to show the best websites to its searchers and any website that takes time to load will deliver a poor experience for users. Nobody likes waiting for minutes for a website to load.
Website speed is directly related to customer experience. Users switch back to search results page when a website takes too long to load, and click on the next search result. All such websites that take time to load lose their rankings eventually when a lot of people click the magical Back button.
Here are a few SEO best practices to reduce website speed.
- Optimize images and compress them. Use GZIP compression.
- Minify CSS, HTML, and JavaScript.
- Make the best use if browser caching.
- Remove redirects.
Don’t take your website speed lightly. You don’t just lose ranking but customers too.
Google Algorithm Updates
Technical SEO Checklist