1. Mobile SEO
According to the Mobile Marketing Association (MMA), in a few years from now, the mobile marketing boom will generate a whopping $400,000,000,000 return.
The massive $139,000,000,000 return enjoyed by the mobile marketing ecosystem today is set to increase at a staggering rate of approximately 52% annually.
Similarly, with the number of global smartphone users reaching two billion this year alone (and predicting to reach six billion by 2020), the Mobile Marketing Association survey not only confirmed the importance of mobile marketing, it also sends a strong message to companies, entrepreneurs, and small businesses, on the internet.
Hence, online marketers are gearing up for this and increasing their budget as well. In fact, mobile ad spending is expected to reach $25.69 billion by 2018.
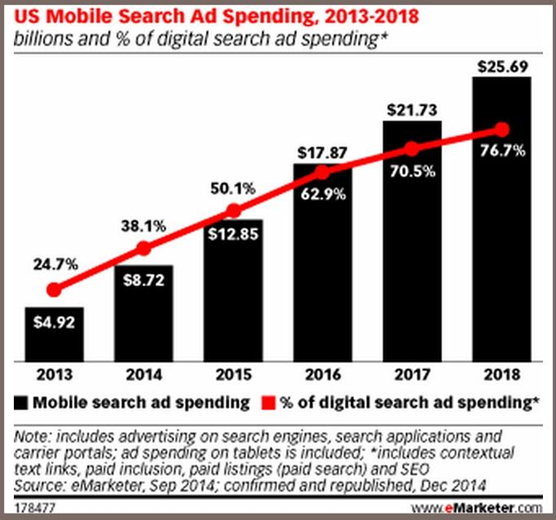
It’s time to create a robust mobile SEO strategy to enjoy the profits of tomorrow. The only way to do this now is to fully optimize your website for mobile.
Here are the four things to do:
1). Make your website responsive: This is very important. A responsive website will detect the mobile device you’re using and then adjust its layout accordingly. This is a one-size-fits-all tactic that allows you to capture your mobile users efficiently.
2). Have a mobile URL: It’s advisable to set up a subdomain for your mobile visitors. This helps to redirect mobile users to the mobile version of the website, and desktop users to the desktop version.
3). Enable dynamic serving: This is a slightly more complicated approach with potential technical challenges especially if you are not a technical guy. This setup helps the server to detect the device and, based on the type of device the user is using, loads the suitable content onto that URL.
4). Boost your website loading speed: In the mobile marketing world, apps earn a large download rate of 45%, while 40% of consumers make a purchase after scanning a QR code.
Also, with 1 in every four online searches being carried out on mobile devices, it becomes indispensable to optimize your website loading speed. After all, studies have confirmed that 57% of mobile users won’t recommend a company that has poor mobile websites.
This makes enhancing your site’s mobile-friendliness an essential marketing effort.
This will equally help you to maintain a positive image in the minds of your consumers.
2. Local SEO
Local SEO is the ability to optimize your products and services to show up for local customers at the exact time they’re searching for them.
Now, if you have been marketing online and follow SEO best practices for the past 2 years, you’re aware of one thing: SEO changes often.
When it comes to local SEO, it’s now more critical that you properly optimize your onsite and offsite SEO for customers and clients who may be looking for your local business in the search engines. When properly optimized, local search can generate more traffic than the typical organic search.
 Local competition is rapidly heating up, and if you’ve not occupied the top of your rankings, you can bet your competitors will outsmart you.
Local competition is rapidly heating up, and if you’ve not occupied the top of your rankings, you can bet your competitors will outsmart you.
Here are some powerful local SEO strategies you can use right now to help your business rank higher for relevant local search terms.
1. Optimize your Meta description and title tags: Meta description and title tags are essential elements that you can customize to mirror your web page content. The text of your description and title tag are displayed in SERPs.
Think of this text as an ad that you need to craft carefully. For example, searching for “hand crafted flowers” in Google shows the title tag and meta description.
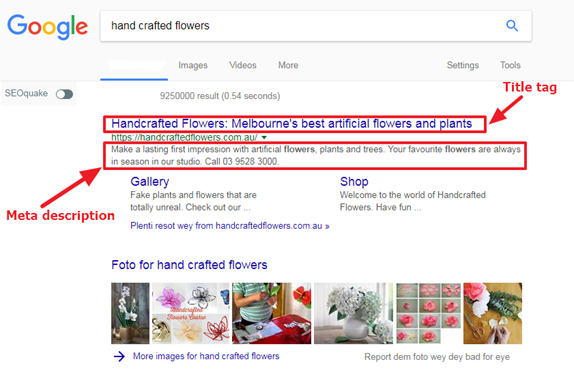
Spend the same amount of time you would spend while crafting an advertisement to writing a great title and Meta description tag. One good practice is to ensure you have your target keyword on both the meta description and title tag.
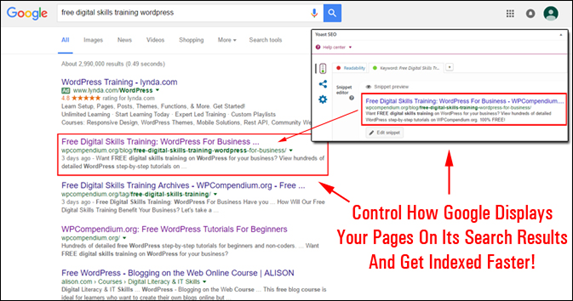
You can use the popular Yoast Plugin to see how these things will look like in Google search:
2). Utilize online business directories and citations: A recent study by Google shows that 4 out of every 5 consumers use search engines to perform local searches. Yet, a lot of small businesses are yet to claim their local business listing on the web, which is sad.
It’s paramount that you get your small business appropriately listed in top online business directories such as:
- Yelp
- Merchant Circle
- City search
Etc.
It’s also advisable to get your business listed on some notable local directories in your area.
Check with your Chamber of Commerce, and your local newspaper’s website to see if they have any local business directory you can get listed on. Also, you can just do a search for terms like “(your city) directory” to further locate other directories and local citation websites.
3). Claim and optimize for Google My Business (GMB): Google My Business is seen as a directory, but I consider it a “big deal,” so it deserves to be given its own section. As a local business owner, it’s very crucial for you to claim your Google My Business (GMB), and Bing Places for Business page.
Here are steps to set up Google My Business Profile:
Step #1: Visit Google.com/business and click “Start Now.”
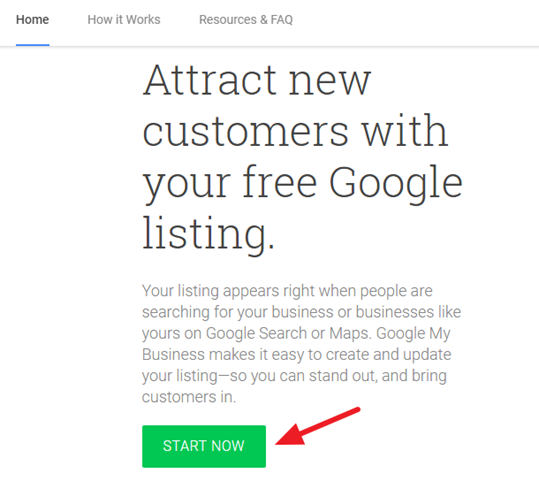
Next, sign in using your Gmail account.
Step #2: Search for your business to see if it’s been added. Search by name and address.
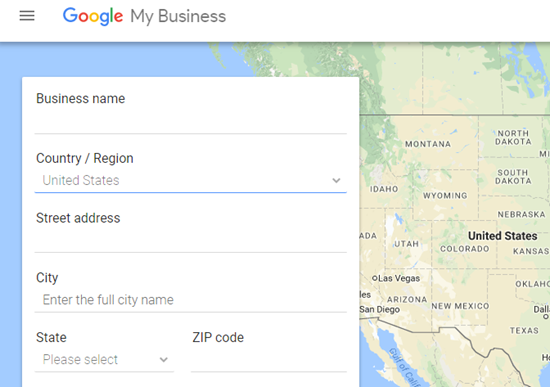
If you’re not offering your services or product to local residents, click on the prompt “Not a local business?”. Then select your business type and through the brand option, you can create a non-local Google+ page.
Step #3: Create your business page if you didn’t find it in the list. Add your correct business name, location, and type. Then agree to “I am authorized to manage this business” to continue.
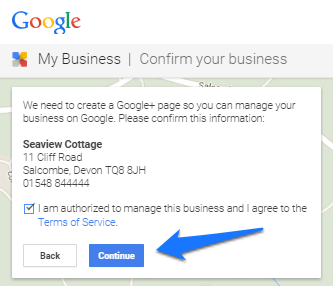
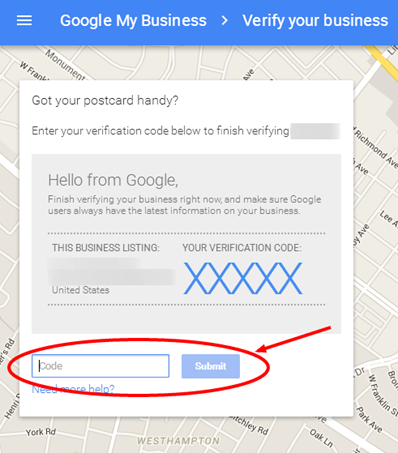
Step #4: For Google will verify your business to ensure it exists, click on “mail me my code” and wait for Google to send it to your business location.
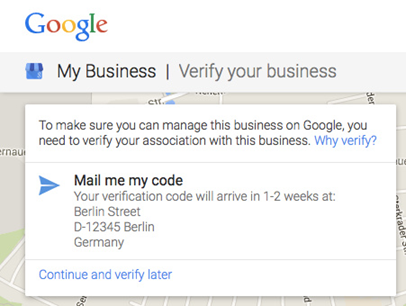
Once you have received the mail, enter the code in your Google My Business Profile to verify it. That’s all. Your business has now been listed in Google My Business page.
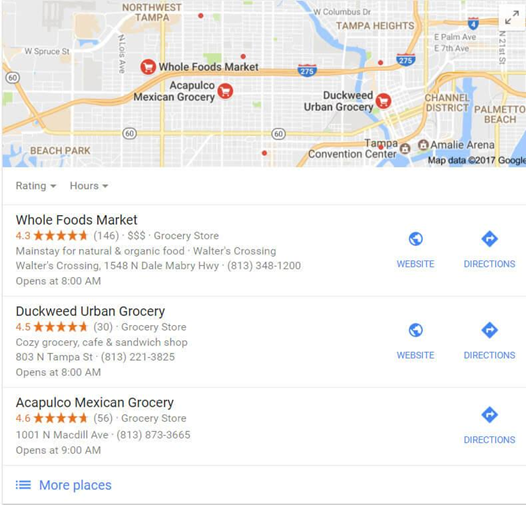
The good thing is that It’s totally free and can get you a massive exposure if you’re well optimized to show up in Google’s local three-pack:
To claim your own Google My Business page, simply go to google.com/business. You’ll need to go through some verification process where Google will mail a postcard containing a PIN to your business’ physical location.
Note: P.O. Boxes are not allowed. Once you’ve gotten the postcard, you’ll simply have to log in and enter the PIN to verify your business, and that’s all.
4). Leverage local structured data markup: “Structured data markup” — often called “schema.org markup” or simply “schema markup” can be added to your website’s code to give search engines more information about your business such as your products, services you offer, the reviews you’ve gotten, star ratings, and more.
A recent statistics show that only 31.3% of websites are utilizing this markup — and even at that, most of them are just using the basics. This is an excellent opportunity to make your local business stand out and possibly crush your competitors in ranking. This can be achieved by adding your structured data markup to your website where appropriate.
Here’s the fact, Google wants you to use structured data markup because it helps their crawlers/bots to understand better what your website content is about.
Google even provides a tool for testing your Structured Data so you can see if your markup is correctly implemented.
5). Use location-based modifiers: In your local SEO campaigns, you can target geographical locations and Zip codes that local customers might search for.
For example, if you have a restaurant and you’re serving local residents in Maryland, you could optimize your pages with search terms like:
- Nearby restaurants in MD, 20707
- Restaurants in Maryland 20708
These search terms might only have <50 searches per month, however, it’ll drive customers who are ready to spend money.
3. Ecommerce SEO
Ecommerce is undoubtedly a BIG industry.
Wondering how big it is?
Well, it’ll interest you to know that in the U.S. alone, the total ecommerce sales in 2014 crossed $300 billion. That’s a growth of 310% over the past ten years:
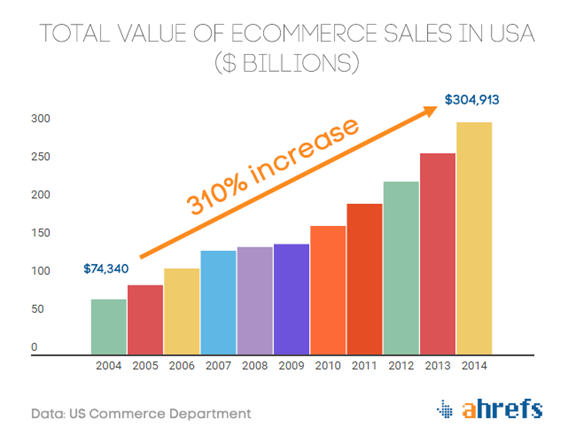
Mind blowing!
However, remember that the competition is equally there. In fact, it was estimated that the number of English language Ecommerce websites in Alexa’s top 1 million is at a whopping 110,000.
And all of these ecommerce-related websites are certainly competing for the top search positions in the market.
So how can you beat the odds and make sure that your ecommerce website gets found in the search engine results pages (SERPs)?
Lets quickly look at few effective SEO strategies that work for an ecommerce website:
1). Keyword research: The starting point of any SEO campaign is keyword research. When it comes to ecommerce SEO, keywords research is even more important. Because consumers use Google to find products and services before visiting the store.
Without adequate keyword research, you’ll be moving blindly – relying on “guesswork” to boost your campaign.
However, this is not a post for keyword research, as that will take its own separate post. But the few things to be mindful of while carrying out SEO for ecommerce-related websites are:
a). Target low competing keywords: These are keywords that are generally easy to rank without burning your fingers. But you also want to ensure that the keywords:
- Have search good volume.
- Are most likely to convert regular searchers into customers.
- Your competitors are NOT targeting.
- You can easily rank for.
b). Visit Amazon to discover some cool buyer intent keywords: Amazon is one of the best places to mine for profitable buyer intent keywords. This is because people literally go to Amazon for the purpose of buying a product(s).
To find good keywords on Amazon, start by entering your seed keyword into the search bar. This is the keyword that best describes your business that you’ll be happy to rank for.
For instance, you could type “Dachshund” and other related keywords will pop down.

Once you do this, Amazon will spit out autofill suggestions as you can see from the screenshot. These are all cool keyword ideas you could target.
There’s also a useful called Keyword Tool Dominator that’s specifically made for Amazon keyword search.
Another good tip is to research competitors’ websites and see what they’re doing.
For this example, we’ll enter “dachshund gifts” into Google:
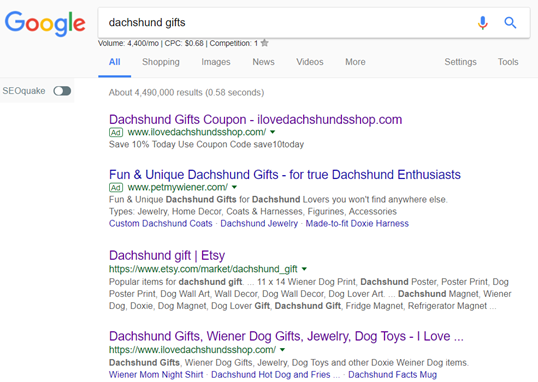
Choose a competitor:
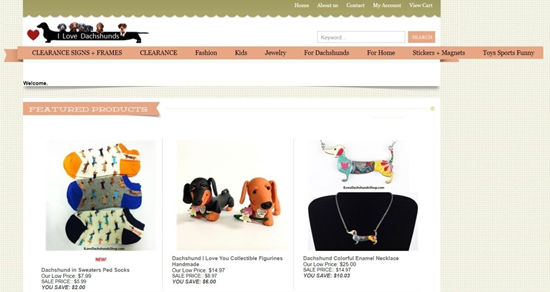
Scan through their product pages and category for potential keywords:
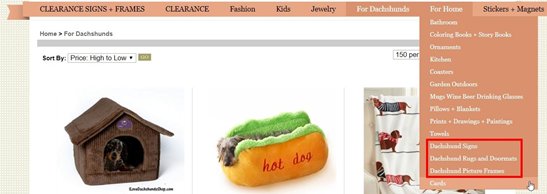
When you’ve gotten enough keywords, the next thing will be to run them through your favorite keyword research tool and select the ones that meet your keyword criteria just like what we stated earlier.
Other things to pay attention to are:
- Use Unique Title Tags for Product Pages: Your title tags must be unique to each product page; this will help to entertain search engine attraction.
- Permanently Carry out a 301 redirect For Expired Product URLs: This will help you to replace the old page in the search engine index with the new one.
- Tweak your Category Pages and Optimize for the target Keywords: It’s a great way to fully prevent the individual pages from competing for the same keywords.
- Mobile-Friendly with a Twist: The search engines are rewarding sites that are mobile friendly.
- Implement Schema Markup to add Rich Snippets to Product Pages: Schema markups help search engines to know your product information and display such product information in search engine result pages, thereby boosting CTRs to the product page.
- Optimize Product Page Permalink and Structure: Remember that the search engines can’t understand nor locate your navigation if it’s not in HTML. So whatever navigation styles you choose to use, ensure it’s in HTML.
- Optimize category pages: A visitor will likely land on a specific product page through the product category page. That’s why it’s important to optimize for these pages.
A page category makes navigation easier for users. And of course, you can have a sub-category as well. Here’s good example from the British Corner Shop.
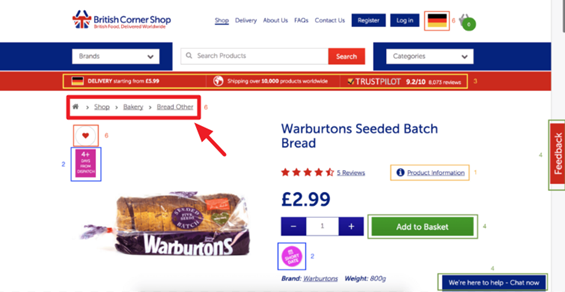
There should be a particular focus for the category. Obviously, you want to display relevant products that are closely-tied to the theme of the category. Including a broad keyword can help you improve organic visibility and attract clicks from visitors to the products themselves.
- Optimize your images: This includes your product images, website header, blog graphics, among many others. Make sure you add a relevant title, Alt Text, and if possible a description of the image or caption.
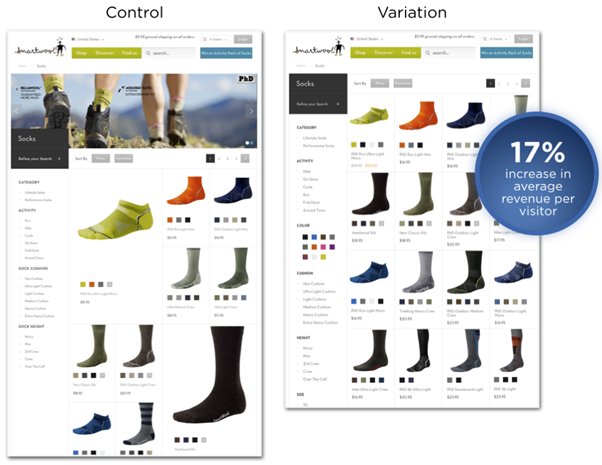
An integral part of image optimization is ensuring that you use high-quality product images in your store. On your own though, you may not know how to position these images or how many of them you should have on your page that will boost conversions. Hence, A/B split testing is the quickest way to get your heads together.
SmartWool conducted an A/B test and found that a more uniform design increased their conversions. They used repetitive image attributes and high-quality product images to enhance better eye tracking when the user is scanning through the list of products. As a result, the company recorded a 17% increase in average revenue per visitor. Trust me, this is the kind of results you will get when you optimize images.
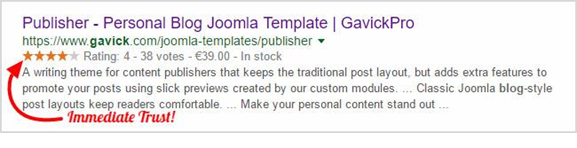
- Using schema to show user ratings, etc.: If you do a Google search right now, you will observe that some sites have star ratings next to their organic listings while others do not. The reason is simple:
The former utilized schema, a new form of optimization technique that can build trust with search users and increase click-through rate by 20-30%.
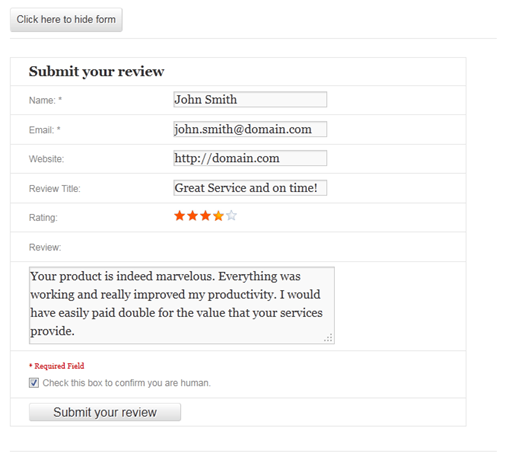
There are several ways to collect reviews and ask users and customers to rate their experience with your product. You can set up your ecommerce shopping system to automatically send an email to new customers, asking them to share their experience.
If you’re a WordPress user, there are plugins that you can use to collect user reviews and star ratings, such as the Customer Reviews plugin. Once you have collected a handful of testimonials, reviews, and ratings, showcase them on your website so that users can find them.
The next stage is to get these user ratings and reviews to rank alongside your website.
This is where you need to schema markup, microdata, or structured data.
Here’s what it does: It helps you to label data in such a way that search engines like Google and browsers like Mozilla Firefox can understand, interpret, and serve them to users.
To get better results, you have to label your address as “business address” and not “where to find us.”
Google will use that business information data on your map listing.
If you don’t want to do this manually, you can install the Structured Data Schema Plugin, fill in the form fields, and have your user ratings appear with your website.
 4. Enterprise SEO
4. Enterprise SEO
Enterprise SEO is simply the process of optimizing a massive website with thousands of web pages while ensuring that the internal principles of the enterprise are maintained in a style that makes stakeholders happy. Enterprise businesses comprise of 500 – 1000 employees.
And both small and large enterprises are investing big time in SEO. According to a survey conducted by Moz, 57% of large enterprise companies have set aside $10,000 which is dedicated to SEO activity each month.
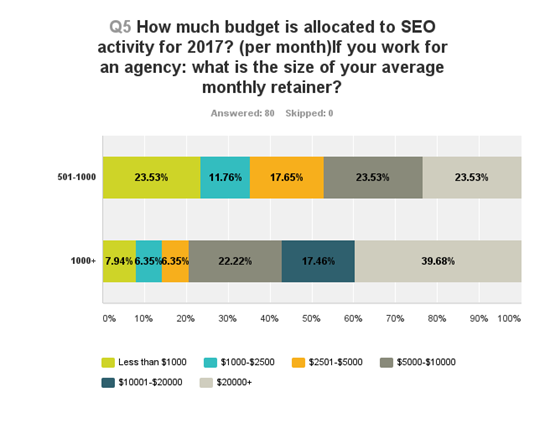
Enterprise SEO, is less about the company size and more about the number of pages, especially when it concerns products or services.
In a nutshell, if your website has from 1,000 products and above, it may be considered an enterprise website.
Using T-mobile as an example. In its tablets and mobile phone support section, Google indexes 41.7k pages while Bing indexes 34.4k pages. It has specific product pages for each device supported by the company.
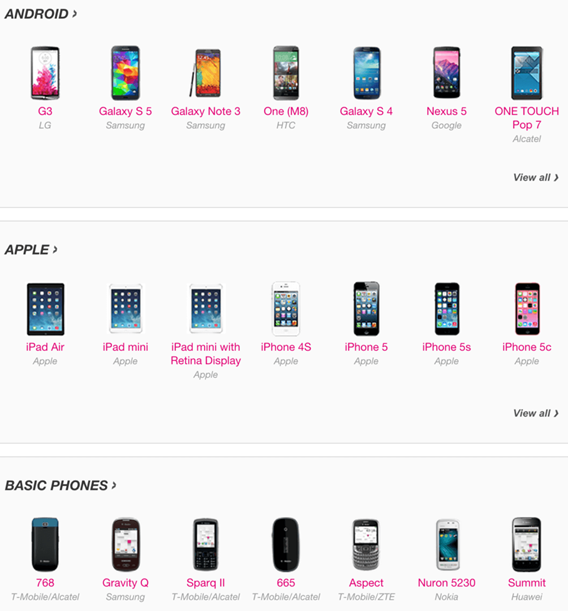
So, T-Mobile is a perfect example — it’s the number of pages it has that makes it an enterprise website, and not the size of the business itself.
Here are four primary hallmarks of enterprise SEO:
- Keyword Selection
- Optimized Templates
- Automated rules
- Fastidious Data Entry
Like all SEO tactics, enterprise SEO starts with proper keyword selection. The concern should be on gathering high-tail and medium-tail keywords that can make good categories and subcategories and can be combined with other words to make long tail queries.
See example below:

Note: Remember that when it comes to Enterprise SEO, the main issues are often linked to website architecture than page level optimization. In other words, how the pages are laid out will determine whether you will succeed or fail in this field.
5. International SEO
When you start thinking of expanding your business overseas, you’ll need to think of how to structure your website in order to equally amplify your online presence overseas.
However, one of the primary considerations when building new multi-country or multilingual websites is how to optimize your website to target multiple languages.
Google Webmaster Tools lists the advantages and disadvantages of the four different ways to structure your website to target multiple languages.
These are:
- ccTLDs: This stands for “country-coded top-level domains.”
- gTLDs: This stands for “generic top-level domains” with subdomains
- gTLDs: This stands for “generic top-level domains” with subfolders
- URL parameters
If you’re considering the best website structure to use, ccTLDs is deemed to have the highest degree of accuracy. However, this is not necessarily the best strategy for all brands. Because there are substantial costs involved with ccTLDs.
To make it easy to understand, I’ll use the following pros and cons chart from SEMrush to explain in what scenarios ccTLDs are appropriate:
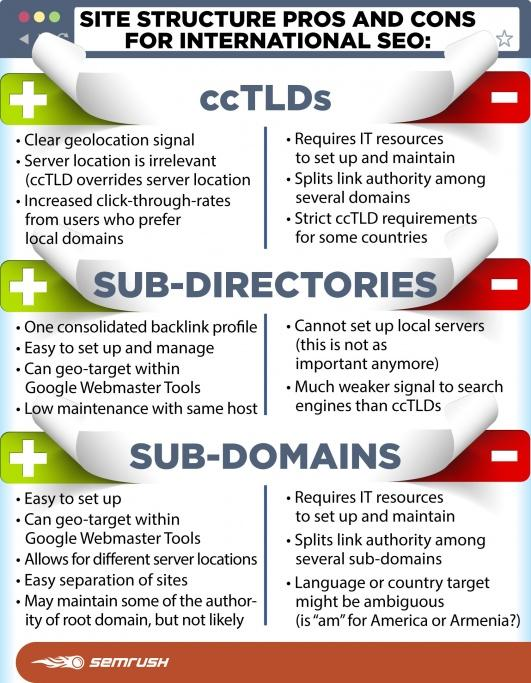
What ccTLDs are Best-suited For
Companies should use this structure if they have:
- Design and development resources to build and run multiple websites, customized for regional audiences.
- A substantial number of audiences in each of their selected countries.
- Resources to create localized, unique content written by expert translators in their local language.
- Different services or product catalogs for each region.
- Funds for massively investing in regional link outreach.
- Are an ecommerce or retail brand that wants to target by countries.
- Offices in the selected countries.
What Subdirectories are perfect For
This is the best option for most companies without a global household brand name and does not have a good amount of content or resources to run multiple websites. It’s typically suitable for an already established website that has a high domain authority and wants to expand into new international markets.
The pros of geo-targeting signals that come with ccTLDs are usually overshadowed by the loss of link authority split among new top-level domains. Based on the fact that it takes lots of effort to build a quality backlink profile for one website, it is also difficult to create quality backlink profiles for ccTLDs.
A consolidated backlink profile is the only advantage offered by subdirectories. Companies should go for this option if they:
- Lack the required resources to build and run multiple sites.
- Want to lower maintenance costs.
- Do not have significantly different services or product catalogs for each region.
- Lacks the funds for investing in regional link outreach
What Sub Domains are perfect for
Finally, this is the best option for companies that desire to keep their brand name in the primary domain but needs separate international websites for internal business reasons.
Conclusion
SEO is indeed a vast topic that keeps changing. If you pay attention to all the information I’ve shared in this advanced guide, you’ll be on your way to creating a more significant impact in your SEO campaigns — driving search traffic and improving your organic search rankings in record time.
You don’t have to implement all at the same time, follow the steps gradually and everything will work out fine.
Could you do me a favor? Please share this in-depth guide with your friends, social media fans, blog readers, customers, and any other person you think will benefit from it. Thank you!
Vertical SEO